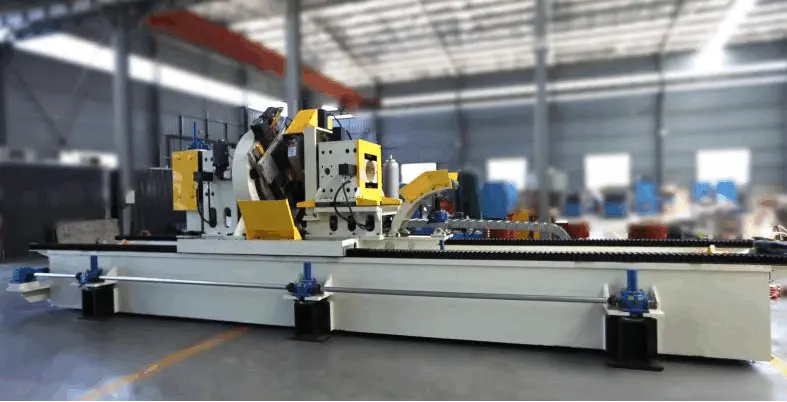
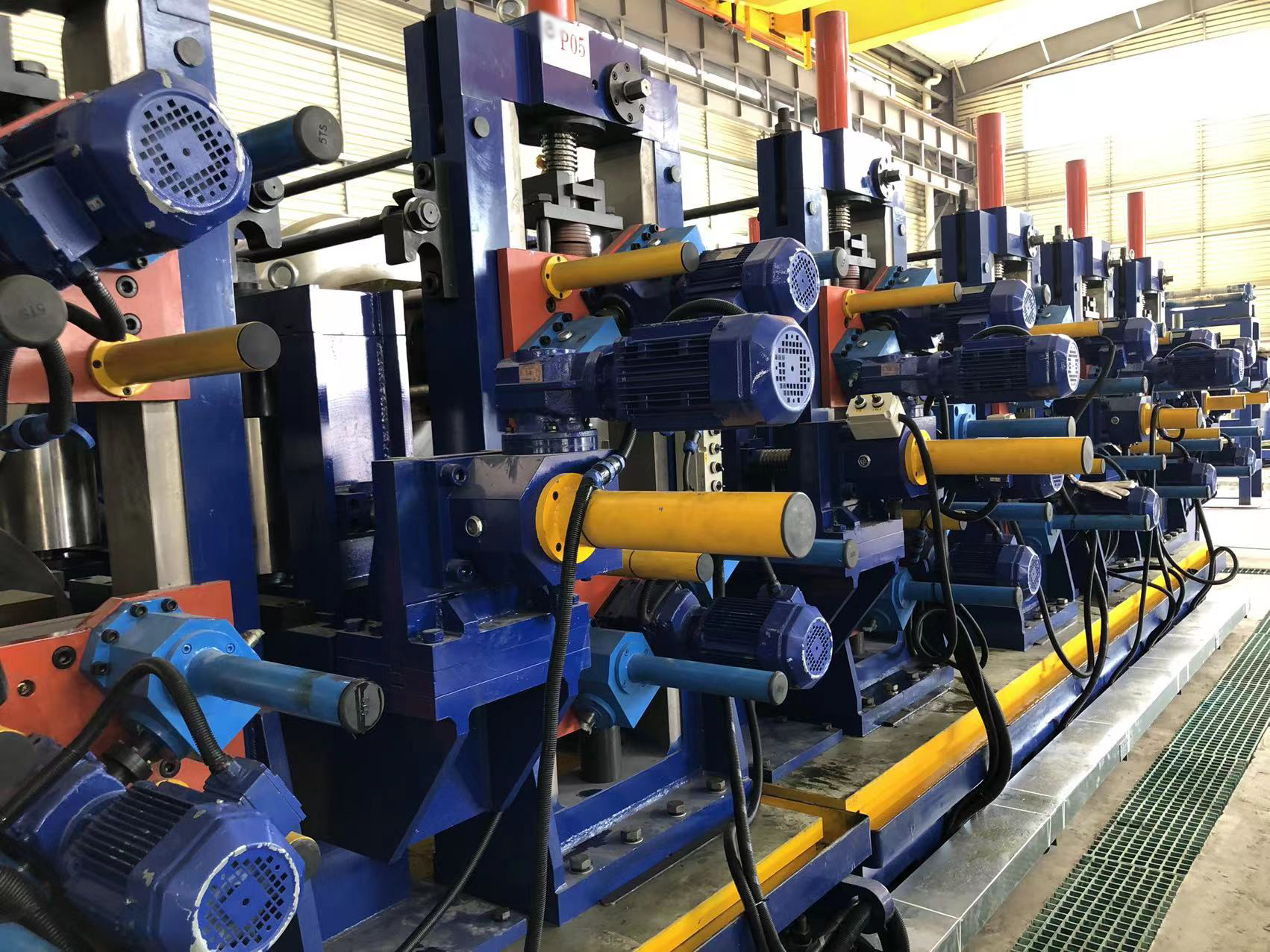
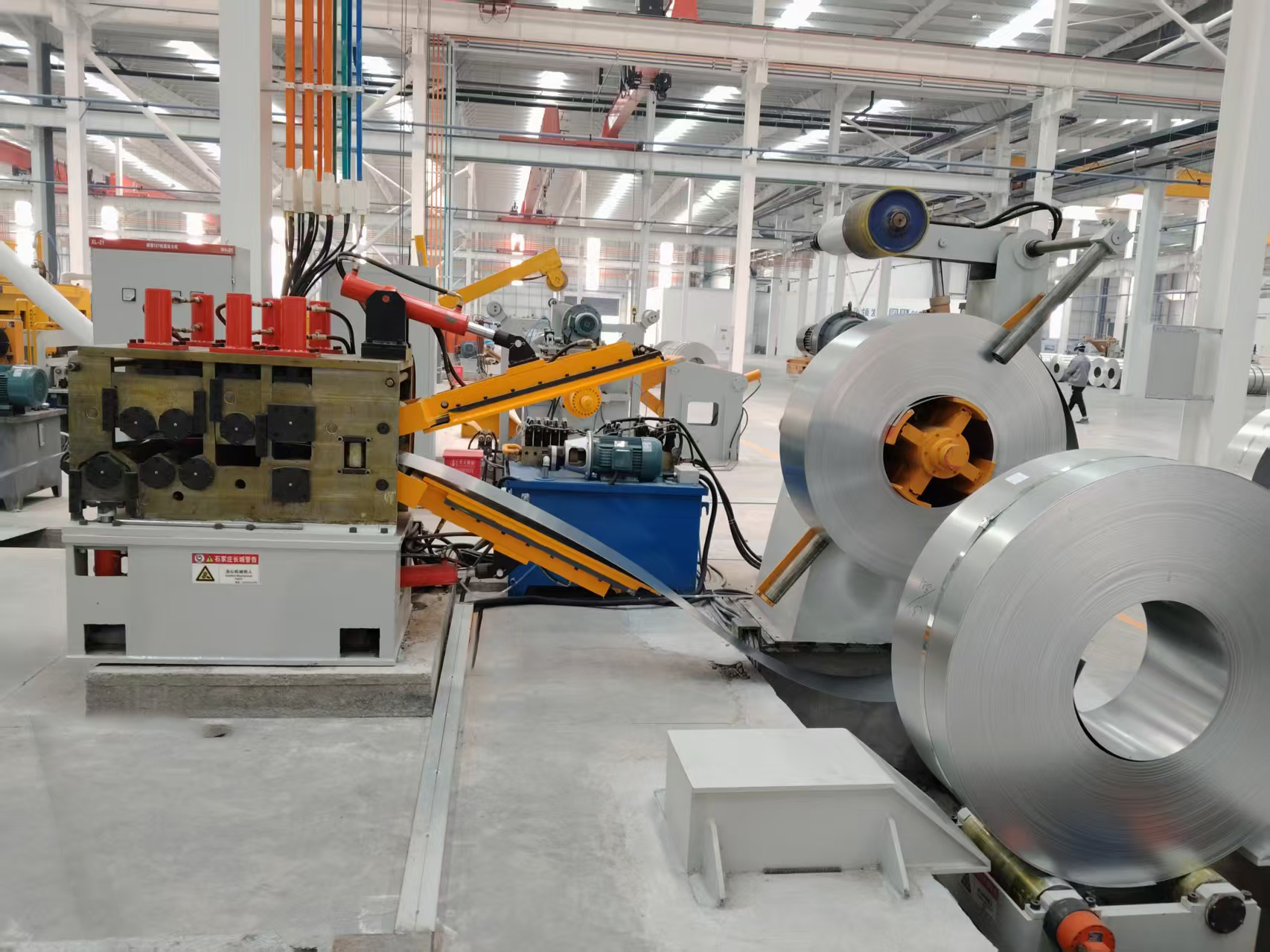
In the high-stakes world of tube and pipe manufacturing, precision and efficiency are non-negotiable. A critical component driving this productivity is the flying saw. This essential piece of equipment is what allows continuous mills to cut products to length without stopping, directly impacting output, material savings, and final product quality. Understanding its role and selecting the right technology is paramount for any operation. Industry leaders like SANSO have consistently refined this technology, integrating it seamlessly with high-performance pipe end finishing machines for complete line solutions.
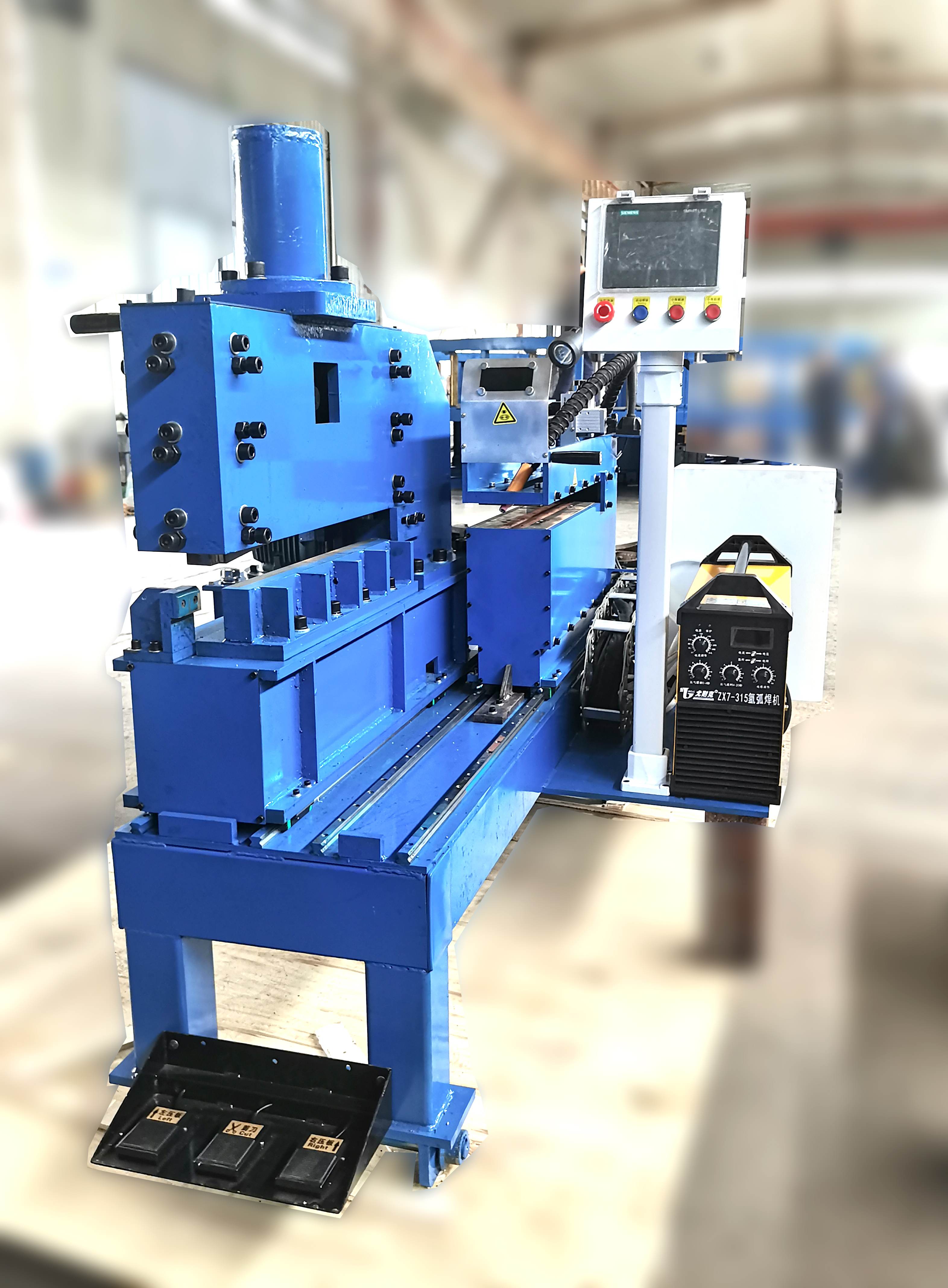

Simply put, a flying saw is a synchronized cutting machine that "flies" alongside moving tube or pipe. As the material exits the mill at constant speed, the saw carriage accelerates, matches the material's velocity, makes a precise cut, and then returns to its start position. This process happens without interrupting production flow. The core mission of a modern flying saw is to deliver clean, burr-free, and perfectly square cuts, which are critical for subsequent processes like threading, grooving, or welding.
The operation is a marvel of synchronization. First, the tube or pipe is measured for length as it travels. This data is sent to the flying saw's control system. The saw carriage then clamps onto the material, perfectly matching its speed. A cutting blade—often carbide-tipped or utilizing cold saw technology—makes the cut. After completion, the clamp releases, and the carriage decelerates and returns. This precise dance ensures minimal vibration and maximum cut quality, a principle that guides the engineering of SANSO's integrated systems.
Implementing an advanced flying saw system offers tangible benefits. The most obvious is dramatically increased production speed, as the line never stops. It also significantly reduces material waste through highly accurate length control. Consistent, high-quality cuts reduce downstream processing time and improve the final product's integrity. Furthermore, modern systems with servo-driven controls offer flexibility, allowing for quick changeovers between different cut lengths and product specifications.
A perfect cut from a flying saw is only the first step. The cut ends must often be beveled, squared, or faced to prepare for welding or other connections. This is where precision pipe end milling machines come in. The performance of the milling machine is heavily dependent on the quality of the initial cut. A poorly cut pipe with excessive burrs or an out-of-square end will cause premature tool wear and inconsistent results in the milling station. Therefore, a top-tier flying saw is not a standalone unit but the essential partner to high-end milling equipment, a synergy deeply understood and leveraged by manufacturers like SANSO.
Selecting a flying saw requires careful analysis. First, consider the material: wall thickness, diameter, and hardness dictate whether a cold saw, carbide saw, or other cutting method is best. Second, evaluate the required cutting precision and surface finish. Third, the maximum line speed of your mill must be matched by the saw's acceleration and tracking capabilities. Fourth, look for robust, wear-resistant construction to minimize downtime. Finally, assess the control system's sophistication—modern digital controls are key for precision and diagnostics.
Regular maintenance is crucial for a flying saw. Daily inspections should include checking blade condition, clamp alignment, and guide rail cleanliness. Lubrication schedules for linear guides and drive systems must be strictly followed. Regularly calibrating the measuring system ensures length accuracy. Keeping the cutting area clear of chips prevents inaccuracies. Proactive maintenance based on the manufacturer's guidelines, such as those provided by SANSO for their equipment, prevents costly unplanned stoppages.
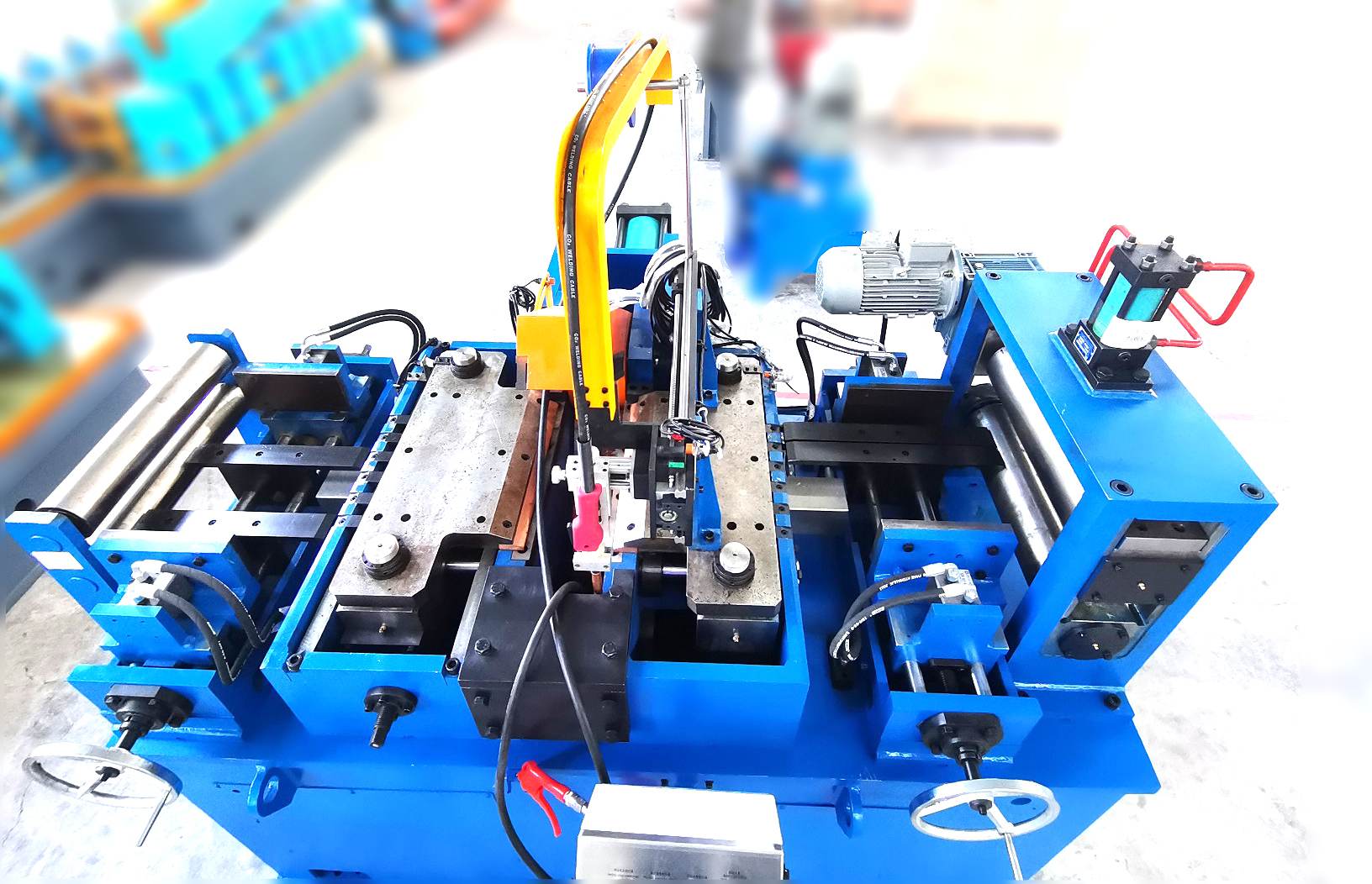
The evolution of the flying saw continues. The integration of IoT sensors for predictive maintenance is growing, alerting operators to wear before failure occurs. Increased use of direct-drive servo motors enhances accuracy and reduces mechanical complexity. Smarter controls with adaptive learning can optimize acceleration profiles for different products. Furthermore, the demand for systems that handle higher-strength materials and offer even faster changeovers is pushing innovation forward, a trend actively pursued by advanced engineering teams.
In summary, the flying saw remains a cornerstone of efficient and profitable tube and pipe production. Its role in enabling seamless, precise cutting directly feeds into the success of downstream processes like pipe end milling. For manufacturers looking to optimize their entire line, investing in a reliable, high-performance flying saw system is a critical decision. Partnering with experienced providers who understand the complete ecosystem, such as SANSO, ensures a cohesive solution that delivers quality, speed, and reliability from the mill to the finished pipe end.
Q1: What is the primary difference between a flying saw and a stationary cut-off saw?
A1: A stationary saw requires the tube or pipe to stop for cutting, creating a production bottleneck. A flying saw synchronizes with the moving material, allowing for continuous, non-stop production at much higher line speeds, which dramatically increases overall output.
Q2: How does the accuracy of a flying saw impact downstream welding processes?
A2: A highly accurate flying saw produces square, burr-free cuts with precise lengths. This ensures perfect alignment during pipe fitting and welding. Inconsistent or beveled cuts from a poor saw lead to gaps, misalignment, and defective welds, requiring rework and increasing costs.
Q3: What are the most common types of cutting blades used on flying saws?
A3: The two most common are cold saw blades (for solid, clean cuts on a wide range of materials) and carbide-tipped circular saw blades (often used for high-speed cutting of thinner-walled tubes). The choice depends on material type, wall thickness, and required finish.
Q4: Why should I consider a branded flying saw solution like those from SANSO?
A4: A specialized brand like SANSO focuses on the precise integration of the flying saw with the entire mill and finishing equipment. This ensures optimal synchronization, control, and after-sales support. Their expertise leads to a more reliable, efficient, and seamlessly coordinated production line compared to a generic or poorly matched component.
Q5: Can a flying saw handle different tube diameters and lengths on the same production run?
A5: Yes, modern CNC-controlled flying saw systems are highly flexible. Through programmable logic controllers (PLCs), operators can input different cut lengths. The system will automatically adjust its measurement and cutting cycle. Quick-change blade housings and adjustable clamps also facilitate handling different diameter ranges efficiently.




